The Fibonacci sequence
Rule
Each term is: Take the sum of the previous two terms
Known as: The Fibonacci sequence
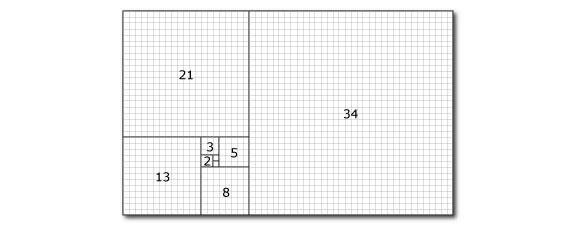
Probably the most famous of all mathematical sequences, which appears in nature, geometry, algebra, number theory, permutations and combinations, and many other branches of mathematics.
Interesting facts about the Fibonacci sequence
* The ratio of last two terms approaches the golden ratio
Because each term is the sum of the two previous terms, squares whose sides are successive terms can be arranged into a spiral as shown above.
The Fibonacci sequence is named after Leonardo of Pisa, known as Fibonacci, who described it in his book Liber Abaci written in 1202.
The Fibonacci numbers occur in many areas of mathematics and science, including biology.
The first 50 terms (starting from n=1) are:
0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55 89 144 233 377 610 987 1597 2584 4181 6765 10946 17711 28657 46368 75025 121393 196418 317811 514229 832040 1346269 2178309 3524578 5702887 9227465 14930352 24157817 39088169 63245986 102334155 165580141 267914296 433494437 701408733 1134903170 1836311903 2971215073 4807526976 7778742049
Example
To get the value for n=11:
- Add my previous answer to the number.
For example, if my previous answer was 10 this gives 21.
So the result is 21.
